“Oxygen-deficient bismuth molybdate nanocatalysts: Synergistic effects in boosting photocatalytic oxidative coupling of benzylamine and mechanistic insight”
Witchaya Phasayavan a,b, Mattawan Japa a,b, Soraya Pornsuwan c, Doldet Tantraviwat d, Filip Kielar e, Vladimir B. Golovko f, Siriporn Jungsuttiwong g, Burapat Inceesungvorn b,*
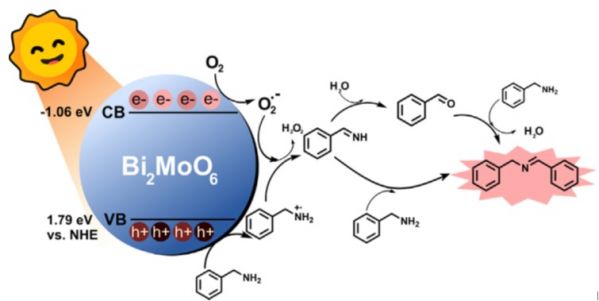
This research is mainly collaborated with Associate Prof. Burapat Inceesungvorn at Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Chiangmai University. Here, Bismuth molybdate (Bi2MoO6) nanocatalysts containing oxygen vacancies (OVs) are found to con-siderably promote the photocatalytic performance toward oxidative coupling of benzylamine to N-benzylidenebenzylamine under visible light irradiation. The structure-activity relationship for this inter-esting catalyst is revealed for the first time. The work offers an alternative facile preparation method to design efficient semiconductor photocatalysts and for the first time reveals a possible benzylamine coupling mechanism over the oxygen-deficient Bi2MoO6 nanocatalyst.
งานวิจัยนี้มีผู้วิจัยหลักคือ รศ.ดร. บูรภัทร์ อินทรีสังวรณ์ ภาควิชาเคมี คณะวิทยาศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยเชียงใหม่ การศึกษานี้ได้พัฒนาตัวเร่งปฏิกิริยานาโน Bi2MoO6 ที่มีช่องว่างออกซิเจน สำหรับเร่งปฏิกิริยาออกซิเดชั่นของสารประกอบ amine โดยกระตุ้นด้วยแสงที่มองเห็นด้วยตาเปล่า และศึกษาความสัมพันธ์ระหว่างโครงสร้างและการเร่งปฏิกิริยาของตัวเร่งนี้ นอกจากนี้ผู้วิจัยได้ศึกษากลไกการเกิดปฏิกิริยาที่ผิวของตัวเร่งนี้ ซึ่งจะเป็นข้อมูลที่สำคัญในการออกแบบวัสดุตัวเร่งปฏิกิริยาแบบสถานะต่างให้มีประสิทธิภาพมากยิ่งขึ้นได้
Reference: J Coll & Int Sci. 2021; 581, 719-728.
